Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that occurs when the body either cannot produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar (glucose) levels, and its malfunction leads to elevated blood sugar levels, causing various health complications. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of diabetes, including its causes, symptoms, types, and management strategies.
Types of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes:
- This type of diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- It often develops in childhood or adolescence.
- People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections for life.
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- The most common form of diabetes, often linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, sedentary behavior, and obesity.
- In type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects.
- Lifestyle modifications, medication, and sometimes insulin therapy are part of the management.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- Occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased needs.
- If not managed, gestational diabetes can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes can increase the risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity contribute to type 2 diabetes.
- Autoimmune Response: Type 1 diabetes is often triggered by an autoimmune reaction.
- Age and Ethnicity: The risk increases with age, and certain ethnic groups are more prone to diabetes.
Symptoms:
- Frequent Urination: Excess sugar in the blood leads to increased urine production.
- Increased Thirst: Dehydration from frequent urination causes excessive thirst.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: The body may break down muscle and fat for energy due to insulin deficiency.
- Fatigue: Insufficient glucose utilization results in fatigue and irritability.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the eyes.
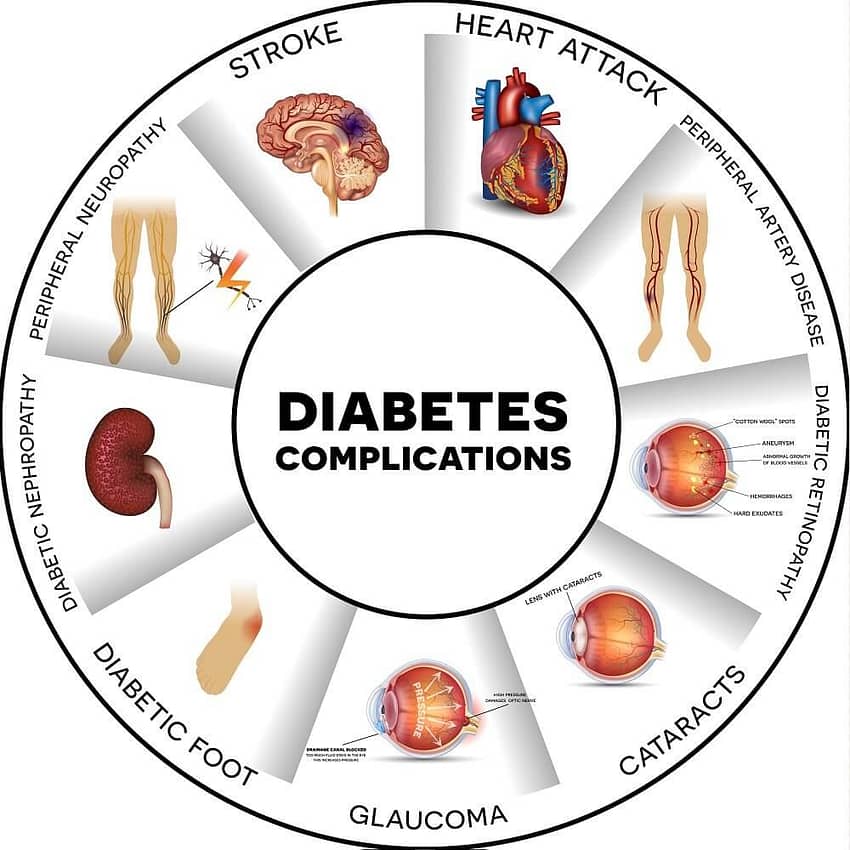
Complications:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Kidney Damage: Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney failure.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Tingling, numbness, and pain in the extremities.
- Eye Problems: Diabetes can lead to vision impairment and blindness if not managed.
Management and Prevention:
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods and sugar intake.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps control blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Medication: Insulin and various oral medications help manage blood sugar levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for effective management.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Quit smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and manage stress.
Conclusion: Diabetes is a serious condition that requires lifelong management. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies is crucial for individuals diagnosed with diabetes. Through lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring, individuals can lead a fulfilling life while effectively managing their diabetes. Early detection, proper education, and a proactive approach play key roles in preventing complications associated with diabetes.